Big Data and Its Business Impacts: Benefits, Challenges, and Use Cases

Have you heard the term “big data”? You probably have. it's an attractive topic that has been starting heated discussions for nearly a decade now. Yet it has never been as relevant as today, with the new data generated in incredible volumes on a daily basis. While the tools that we developed to process data struggle to deal with the constant flow of data, businessmen and data scientists alike entertain the idea of how to get the most out of big data. In this article, we would like to discuss a few essential things about big data:
- What is big data?
- Big data and its business opportunities
- Major challenges of big data
- A few practical use cases for big data in business
What Is Big Data in Business?
The conventional data management systems and data processing applications can no longer deal effectively with the growing amount of data created by human civilization. That's where the term of big data comes from. It doesn't refer to any specific number; rather, it is used to emphasize the core characteristics of the data:
Big data is the data that is too big, too fast, and too hard to process via conventional or available resources. Click to TweetThis means that the volume, as well as the speed of accumulation of the data, grows while the time window when the data stays relevant, shortens. As most big data in business is generated in real-time, it must be processed quickly in order to stay valuable.
There are three main sources that generate big data:
- Business: the data is produced by companies in huge volumes on a daily basis. This can be financial data (invoices, transactions, billing data), internal and external documentation (reports, business letters, production plans), and so on. The creation of big data is especially relevant for organizations that convert from analog to digital workflows.
- Communication: this is the data that you as a person create. Social media, blogging, and microblogging are all major sources of communication data. A new photo, a text message, or a search query, when collected en masse, all add to the increasing volumes of big data.
- IoT: this data is sensor-generated. The smart devices use their sensors to collect the data and upload it to the Internet in huge volumes. A few examples of sensor-generated data include CCTV logs, robotic vacuum cleaners, data from weather stations, etc.
So big data basically refers to large data sets collected from a variety of sources. They can be used to reveal patterns, associations, or trends, to analyze them, and make complex predictions. With this understanding in mind, let's take a look at big data and its business impacts.
Impact of Big Data on Business
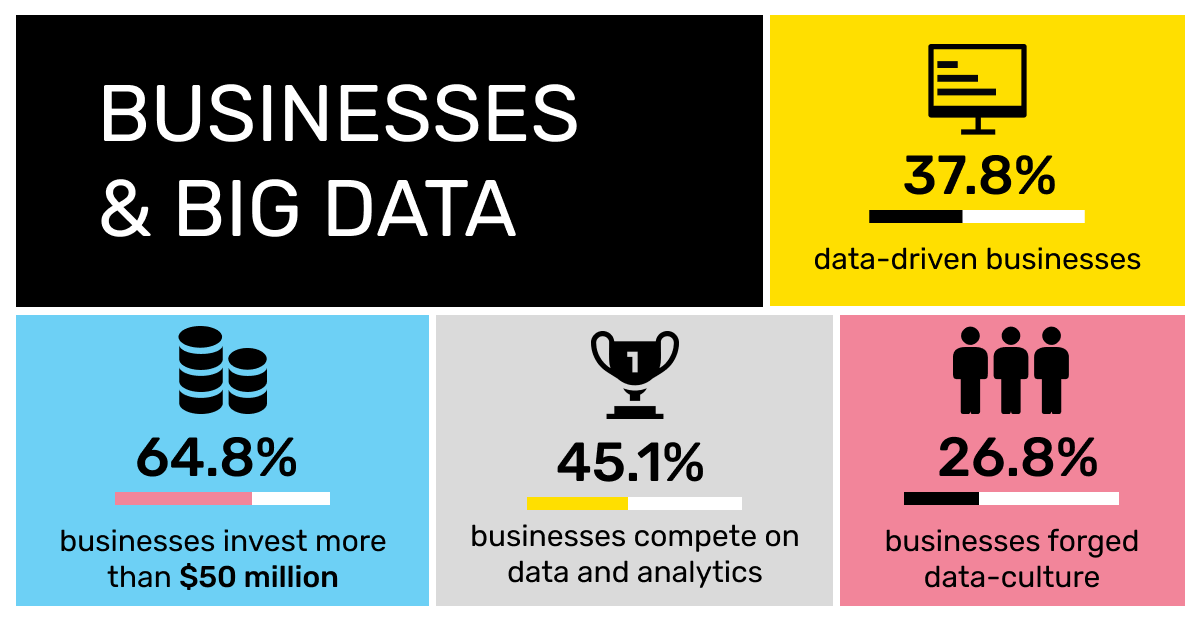
While the big data phenomenon determines the current informational landscape, its impact on business has reached unprecedented rates. As NewVantage Partners report in their AI Executive Survey, 98.8% of leading companies confirm investment in artificial intelligence and big data capabilities. Moreover, by 2023, big data and business analytics revenue will reach $274.3 billion worldwide according to research by Statista. it's half as much again as the revenue from 2019 and more than 4 times the revenue from 2018.
In a way, big data defines the golden rule of modern AI: the more data you have, the better your predictions will be. The benefits that big data brings are plenty, yet most importantly, we should mention the three main ones that motivate the majority of big data investment.
Quality
As modern companies permanently seek competitive advantages, big data helps with better, more precise target marketing through advanced data analytics and improved decision-making. It offers ways of improving the quality of products and services. Big data facilitates monetization by providing a better understanding of the clients’ needs. It helps to adopt a more personalized and focused approach, to cut time, and increase the efficiency of business processes. Altogether, such adoption of big data results in a higher quality of products, enhanced customer experiences, and more satisfaction from the clients.
Cost
Data-driven AI projects are commonly developed for the sake of workflow automation benefits. Giving the tedious and mundane tasks to the machines frees the human experts and allows them to focus on the value-adding business goals. Big data helps to look for new ways to reduce costs by improving the efficiency of existing business processes. This improves time management while increasing speed to market. Combined with high quality, big data opens the path to increased revenues and sustainable economic development for businesses.
Analytics
This is where the part about better predictions kicks in. Big data allows you to see not just a pattern within the industry or a process you consider. And when we say ‘see’ we mean literally: data visualization is one of the perks that are only possible with big data. It paints the bigger picture and, driven by the larger scope of associations and trends, helps you answer the most important question: why something happens the way it does. Big data gives context by showing the data in permanent motion, 24/7. It leads the way to improved decision-making as big data provides insights about hidden patterns. For this reason, big data is commonly used by businesses for predictive analysis and making weighted, well-informed decisions.
Big data provides intelligent business insights that promise not only economic but also social benefits. it's only natural that the demand for big data from businesses grows.
Challenges of Big Data
Still, as the advantages of big data are undoubtedly attractive, it's also important to note they often come hand in hand with a set of challenges. Firstly, big data is hard to process. As we've mentioned above, it's big and fast, which means it requires specific tools to become truly useful for a business. However, the correct tools are not easy to learn, nor they are cheap. This means that a business will have to be prepared for the financial, human, and time costs to be paid for the correct integration of big data into operational processes.
Moreover, big data is also highly variable. It may come as photos or texts; it may be structured or unstructured. Big data variability increases the potential value by widening the pattern-extracting opportunities, it also complicates the processing, annotation, and training. If you’re interested in learning more about the complications that big data brings to business processes, we've already talked about it in our article about big data and the crisis of AI.
it's also worth remembering that there are risks connected to the uncertainty of big data. As it becomes harder to pre-process the incoming stream of data, the level of confidence in its validity precipitously drops. Big data that you cannot trust is both useless for training, as well as harmful for the automated ML algorithms aimed at data processing and model training.
Yet it's being argued today that the toughest challenge of big data is found not among its features like variety or uncertainty. 90.9% of businesses that made the first steps to adopting big data culture cite people and processes as the major barriers to become truly data-driven. Data science skillset is not the easiest to obtain, and people need time to understand and get motivated for learning it. Besides, big data and AI alike still lack the procedural support that is essential for their wide-spread implementation. For now, a lot of businesses adopt the waiting attitudes since they cannot afford the impressive cost of investing in big data. it's still a high risk/high reward area that requires proper regulation to become undeniably profitable.
Big Data Uses in Business
If there are so many challenges to implementing big data, why invest in such a troublesome enterprise? Before you make up your mind, let us tell you more about how to make the most of big data in various businesses.
Big Data in Retail and eCommerce
The major goal of any retailer, whether online or offline, is to learn how to predict customer behavior. Armed with such knowledge, a business can handle the increasing rush of competition. Yet, as the world grows and gets more globalized, it becomes harder to make sense of the variety of data floating around.
That's why big data is hugely important in retail and eCommerce. Tiny details such as a like, a share, a repost, or a comment can have key significance for understanding the behaviors of customers. In addition, the scope of sensor-generated data (collected from POS terminals, for example), can shed light on the hidden trends, which enables control over the current situation, as well as prediction of the future ones.
Besides, as consumers become more picky and knowledgeable about their opportunities, it's very important to look for ways to make customer journeys more personal and attractive. Immersive customer experiences gain weight in modern retail precisely because people do not only come for buying stuff. Shopping based on the implementation of big data can be transformed into a fun activity in its own right, with augmented reality with gamification elements playing significant parts in building relationships with customers.
Big Data in Marketing and Advertising
Personalization is the key to success. Modern businesses are depending on perceptive client-centric data-based strategies that take into consideration what customers need and want. Today, segmentation of the market and targeting are essential practices for any type of business.
Smart implementation of big data allows taking the game to the next level. With the huge volumes of data collected from the customers (including their purchasing behaviors, search queries, social media history, etc.), it's possible to make accurate predictions that can be implemented in multiple scenarios. Big data allows businesses to understand what type of products to advertise to whom and in what ways in order to inform the customers in proactive and attractive ways.
Complex ML algorithms designed for big data input help to build marketing strategies that not only benefit businesses but also individual consumers. People are able to find the products and services they require faster and in more convenient ways, without the need to browse through thousands of available options.
Big Data in Finance and Banking
Artificial intelligence has been adopted as a partner for the financial industry for a long time now. Large hedge funds and leading banks use AI for forecasting and analytics that cannot be performed without the help of the machines. With big data, the financial industry gains access to new possibilities.
Algorithmic trading is one area of finance that has been using AI since its invention. However, if the traditional ML tools were able to perform fast deals, big data has provided them with much-needed context. Trade is migrating to a new understanding: from buying low and selling high to gaining the recognition of how external circumstances affect the most minute of the transactions. Social, economic, and political factors all play the role in forming prices, and models working on big data identify the surreptitious connections that help with long-term strategies.
Similar to building trading strategies on a stronger forecasting basis, private consumers benefit from the introduction of big data into financial and banking services. The analysis made with access to large volumes of data introduces new approaches to the evaluation and promotion of financial health. Algorithms that use data integrated from a variety of areas (not only banking and investment data but also social and buying behaviors) help design personalized plans to look for past errors and misconduct, as well as avoid potentially risky behaviors in the future.
Big Data in Logistics and Transportation
Per definition, logistics is a very nuanced industry. Similarly, transportation deals with a lot of data that takes into consideration the factors of volume, weight, availability of resources, and, most importantly, time. The primary goal of businesses in these areas is to calculate everything and make sure there is no downtime or idleness. Naturally, big data is at the core of operational planning as the ever-increasing volumes of data collection demand intricate algorithms and a lot of computational power to process, analyze, and provide the most efficient solutions.
Safety is yet another concern that big data helps to deal with, and this is especially apparent in the area of private-sector transportation. Self-driving cars are a great example of technology that absolutely requires big data to develop. The multitude of factors that impact the evaluation of the road situation makes this task impossible for the conventional ML models. There is a need for accurate and comprehensive data to facilitate AI decision-making. The introduction of such systems as LiDAR expands the volume of data and allows better and faster control of the surrounding, which ensures the safety of the passengers. If you’re interested to learn more about this topic, follow the link to our article on big data as the driving force of autonomous vehicles.
Big Data in Natural Resources
While industries such as marketing, retail, or transportation may have their large players, it's natural resource mining that is arguably the most complicated for smaller businesses to enter. As a result, just a handful of big companies that extract natural, primarily energy resources (coal, oil, and gas) compete for their share of the market. The scale of these businesses is dictated by the numerous mines, wells, drills, and rigs that all operate within their complicated ecosystems, with working flows being inherently complicated by the warehousing, logistics, transportation, and other operations.
Using machines to manage operations is only natural. Yet at such volumes, it's important to optimize every insignificant piece of data that can save as a source of either great savings or comparably great losses due to the economies of scale. Algorithms trained on big data is what helps to take the immense flow of operational data for these companies under control.
Additionally, the expansion strategies and prediction of production are also supported by the big data. Looking for the reservoirs of natural resources is extremely expensive, and big data with its precise forecasting allows to save a lot of time, money, and efforts that would otherwise be spent drilling the barren rock. Big data encompasses a wide range of information from existing databases to prices fluctuations to weather forecasts to calculate the feasibility of investment in the development of platforms and the extraction of natural resources.
Big Data and Business: Final Thoughts
The volume of data generated by human civilization grows exponentially every day. The social media people use, the data generated by the IoT sensors, the data collected by businesses all add to the big data phenomenon that encompasses every small detail of our lives. Learning how to use this big data is a challenge for modern businesses, mostly because it's hard to process and fast to lose relevance. However, when done right, big data can bring significant competitive advantages.
Big data helps to increase the quality of products and services while reducing costs. It makes the processes more efficient and allows building comprehensive user journeys to enhance customer experiences through personalization and accurate targeting. Besides, big data is used for improved analytics and finding hidden patterns and associations. This brings not only economic but also social benefits for both businesses and individual consumers.
And there is virtually no industry that ignores big data. Retail uses it to predict consumer behaviors. Advertising personalizes offers in search of an ideal client. Finance designs more elaborate and comprehensive trading algorithms. Logistics and transportation depend on big data to manage operational minutiae and increase safety. Big data impacts every business, and it looks like this trend will only continue growing.
Big data is a complex yet flexible and inherently advantageous tool in the right hands. It offers a lot to those who can overcome its challenging nature. A business seeking the opportunities provided by big data should be ready to learn how to collect and process it, as well as how to use it to annotate it and train their algorithms. We will continue discussing the topic of big data in the future. Subscribe now to stay tuned!
Written by
Karyna is the CEO of Label Your Data, a company specializing in data labeling solutions for machine learning projects. With a strong background in machine learning, she frequently collaborates with editors to share her expertise through articles, whitepapers, and presentations.

