DeepSeek OCR: Why Performance Breaks Down on Real-World Documents
Table of Contents
- TL;DR
- What is DeepSeek OCR?
- DeepSeek OCR Context Limits: When 8K Tokens Isn’t Enough
- Why DeepSeek-OCR Struggles with Complex Layouts and Table Recognition
- Training Data Requirements for Production-Ready OCR
- DeepSeek OCR: How to Use for Text Extraction Tasks
- DeepSeek OCR vs Traditional OCR: Performance Comparison
- What Production DeepSeek-OCR Deployment Actually Requires
- About Label Your Data
- FAQ

TL;DR
- DeepSeek OCR hits 97% on benchmarks but drops to 75-80% on financial documents, with table misalignment causing 30% of production failures.
- Training on 300K pages per language misses critical edge cases (watermarked scans, dense layouts, domain formats) that cause most real-world errors.
- 1,000 expert domain annotations outperform 10,000 auto-labeled clean PDFs for closing the production accuracy gap.
What is DeepSeek OCR?
DeepSeek OCR is an OCR deep learning vision-language model (DeepSeek-VL2) that extracts text from document images in 100+ languages. According to the DeepSeek OCR paper, it achieves 97% benchmark accuracy but experiences 15-25% degradation in production on complex layouts and domain-specific documents.
Production teams report context overflows, table parsing failures, and accuracy degradation on financial documents despite strong benchmark results. The model trained on 30M pages across 100 languages, yet struggles with dense layouts in real-world deployments. At compression ratios above 10x, accuracy plummets from 97% to 60%.
Documents with 1200+ text tokens achieve only 59.1% precision at 64-token mode (unusable for production).
The gap is training data. Benchmark machine learning datasets miss production variability: edge cases, domain-specific structures, scan quality issues, and business document complexity. The model’s own data shows this: slides need 64 tokens for good performance, newspapers need 795+ tokens — a 12x difference based on training representation.
Understanding where DeepSeek OCR fails reveals how training data quality determines production success.
DeepSeek OCR Context Limits: When 8K Tokens Isn’t Enough
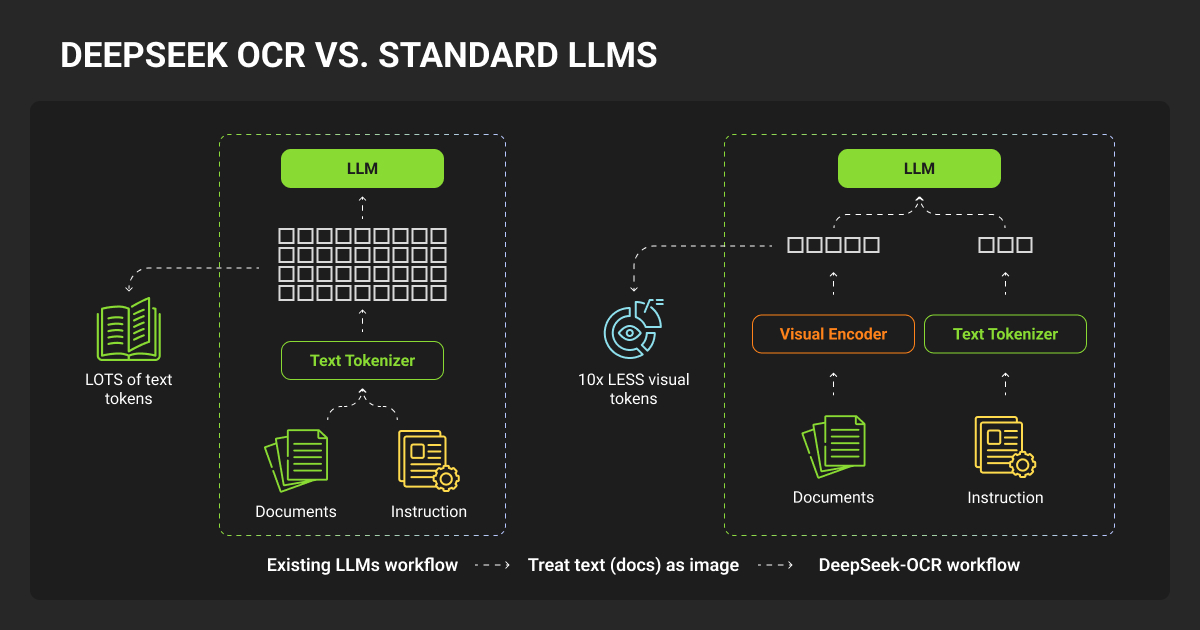
DeepSeek-OCR contexts optical compression achieves an 8K token window, but this creates production failures invisible in benchmarks.
Context overflow causes hallucination loops. Deployment teams report bank statements generating “cheerleader stories” and models becoming “totally unusable” after hitting limits.
The compression accuracy cliff:
| Token Range | 64T Accuracy | 100T Accuracy | Compression | Production Status |
| 600-700 | 96.5% | 98.5% | 10.5x | ✅ Usable |
| 900-1000 | 85.9% | 96.8% | 15.1x | ⚠️ Degraded |
| 1200-1300 | 59.1% | 87.1% | 19.7x | ❌ Failed |
Above 10x compression, accuracy crashes. Documents with 1200+ tokens achieve 59.1% precision — completely unsuitable for production systems requiring 95%+ accuracy.
Training data reveals the root cause
30M pages across 100 languages means only ~300K pages per language. Like most machine learning models, DeepSeek OCR’s production performance depends on training data quality and distribution.
Training focused on standardized documents (70% OCR data from academic papers and books, fixed 8,192 token sequences).
Critical gaps in training coverage:
- Dense financial reports (tables + footnotes + small fonts)
- Multi-column newspapers (4,000-5,000 tokens)
- Watermarked documents and partial scans
- Language-specific density
- Real scan artifacts versus clean PDFs
DeepSeek OCR model evaluation confirms the bias: slides need only 64 tokens for good performance, while newspapers require 795+ tokens — a 12x difference based purely on training representation.
Quality data annotation bridges the gap through strategic coverage rather than volume. Density spectrum annotation spans 500-token simple forms through 4,000+ token dense documents, with native language annotators capturing compression pattern differences.
Edge case coverage targeting watermarks, degraded scans, and unusual layouts addresses the 15-20% of production volume that causes 60-80% of failures.
Expert annotators recognize density boundaries, understand domain-specific information packing, and provide native multilingual quality. Result: 1,000 strategically annotated edge cases outperform 10,000 auto-labeled clean PDFs for production robustness.
Learn more about effective document digitization with OCR strategies for production systems.
Why DeepSeek-OCR Struggles with Complex Layouts and Table Recognition
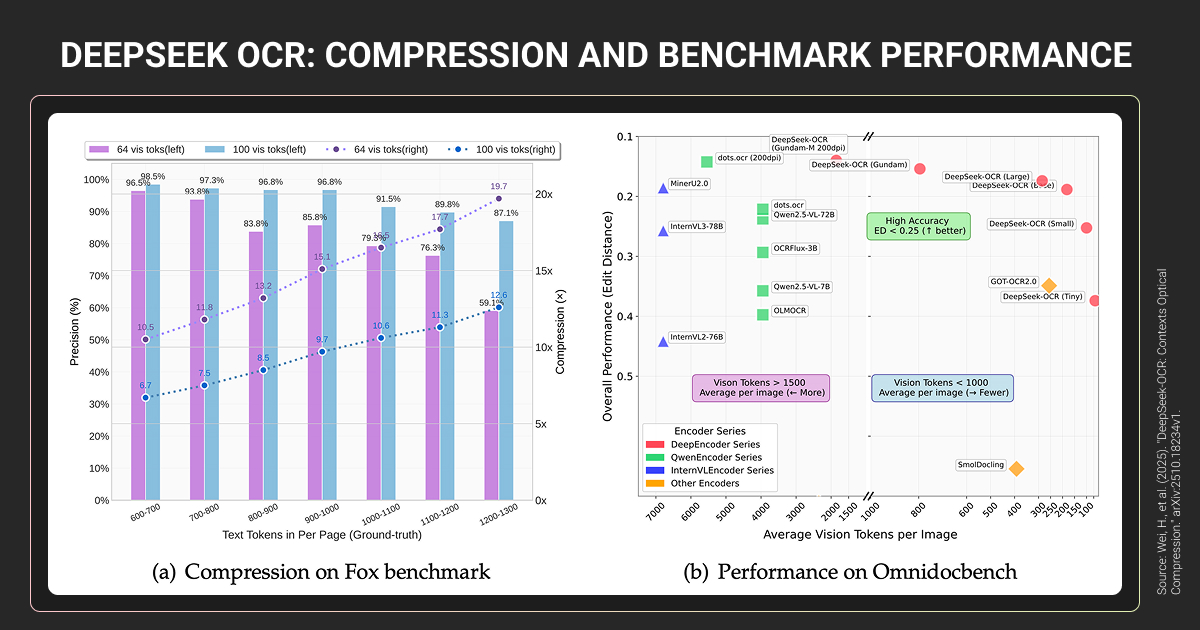
Despite 0.127 edit distance on OmniDocBench, production deployments reveal structural failures. Financial statement testing showed “unstable outputs with hallucinated text and unreliable structure preservation.”
Error breakdown in complex documents
| Error Type | % of Errors | Impact |
| Table misalignment | 30% | Columns scrambled |
| Header contamination | 20% | Headers as content |
| Column order | 18% | Multi-column broken |
| Character errors | 15% | OCR mistakes |
| Word-level | 10% | Missing/added words |
Financial reports: 0.289 edit distance (production) vs. 0.134 (benchmark) — nearly 2x degradation.
Benchmark performance
- DeepSeek Small (100 tokens): 0.221 vs. GOT-OCR2.0 (256 tokens): 0.287
- DeepSeek Gundam (795 tokens): 0.127 vs. MinerU2.0 (6,790 tokens): 0.133
- Result: 8.5x token efficiency advantage
Production reality: MinerU maintains 90.67 layout preservation where DeepSeek degrades to 75-80. Traditional pipelines win on complex structures through specialized components (dedicated layout detection, table recognition, text extraction models).
Training data gap: OCR 2.0 data includes 10M synthetic charts (matplotlib-rendered, not real business charts), 5M chemical formulas, 1M geometric figures. Financial documents underrepresented — causing 15-25% production degradation.
Annotation requirements for production accuracy
Financial documents need domain expertise: SEC filing formats, nested tables, footnote relationships, multipage continuations. Automated tools (PP-DocLayout, MinerU) miss semantic relationships.
Multilingual layouts need native speakers: text flow direction (Arabic right-to-left, Japanese vertical), mixed scripts, cultural conventions. Unicode errors prove automated labeling fails without native verification.
Quality beats volume: 1,000 expert-annotated financial documents outperform 10,000 auto-labeled academic papers for domain accuracy in OCR data extraction workflows. Human verification captures semantic relationships, domain conventions, and hierarchical structures that automation misses.
Training Data Requirements for Production-Ready OCR
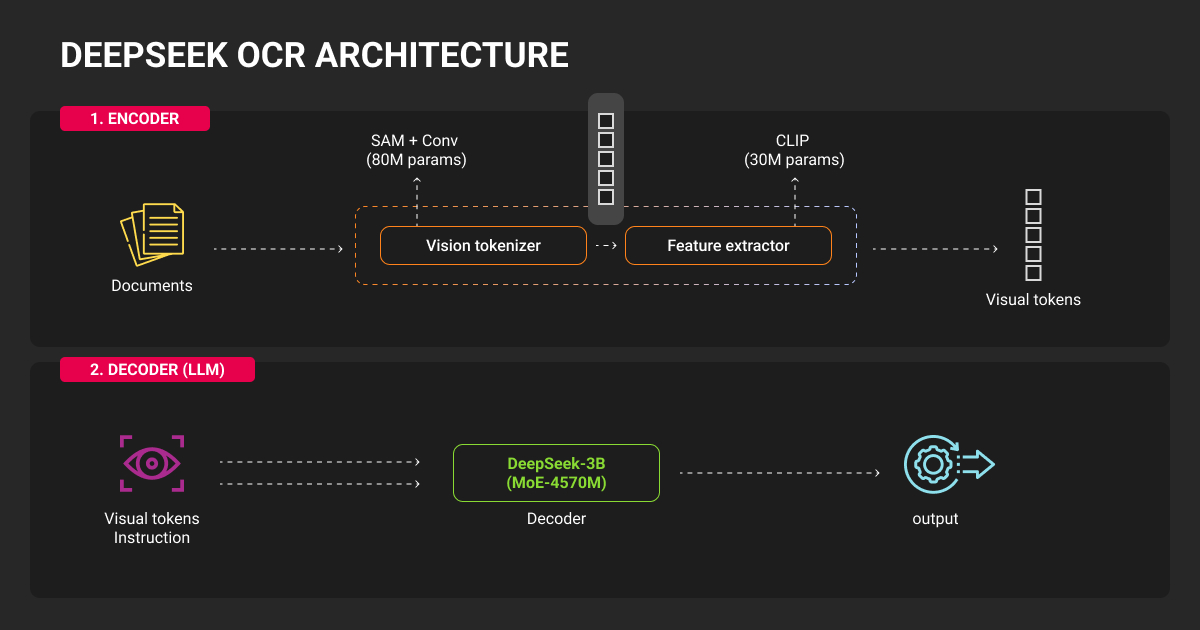
DeepSeek’s 30M pages across 100 languages sounds impressive, but 300K pages per language provides thin coverage. Performance varies 10x by document type based on training representation: slides need 64 tokens, newspapers need 795+ tokens.
Training composition breakdown:
- 70% OCR data (standardized documents)
- 20% general vision data
- 10% text-only data
- Fixed 8,192 token sequences
- No disclosed domain distribution (financial vs. academic vs. legal)
What quality annotation provides beyond volume
Edge case coverage
Fox benchmark tests clean 600-1,300 token documents. Production includes degraded scans, decorative fonts, watermarks, partial images, and poor lighting — scenarios causing 60-80% of failures despite representing only 15-20% of volume. Native speaker validation prevents Unicode errors in multilingual systems.
Domain-specific expertise
Financial documents require understanding:
- SEC filing structures and GAAP compliance
- Nested tables and footnote-to-table relationships
- Multi-page continuations without headers
- Numeric precision (99.99% accuracy required vs. 99.9% acceptable for text)
Production evidence: financial documents achieve 75-80% layout accuracy with base model vs. 90%+ with domain-specific fine-tuning on 500-2,000 labeled examples (5-15% improvement).
Medical documents need HIPAA-compliant workflows, terminology accuracy (dosage errors create safety risks), and laboratory report structure understanding. Technical/legal documents require hierarchical formatting, citation accuracy, and exact text preservation.
Multilingual authenticity
Native speakers provide:
- Cultural layout understanding (Japanese vertical text, Arabic right-to-left flow)
- Script-specific expertise (Arabic diacriticals, Korean mixed systems, Devanagari ligatures)
- Context-aware domain terminology (not machine translation)
- Mixed-script document handling (Southeast Asian business docs mix Thai, English, Arabic numerals)
Quality threshold: Inter-annotator agreement (Cohen’s Kappa) >0.75 indicates reliable training data; financial annotation typically requires >0.85.
Flexible service models
Production-focused data annotation services provide:
- Pay-per-object data annotation pricing (no annual commitments)
- Tool-agnostic workflows using document annotation tools (works with vLLM, Transformers, custom implementations)
- SLA-backed quality guarantees (penalties for annotation errors)
- Flexible scaling (2-15 FTE based on project phase)
- No vendor lock-in (data portability across OCR frameworks)
DeepSeek OCR open source release under MIT license enables self-hosting without API costs.
This enables validation on 500 domain documents, identifying gaps, commissioning targeted annotation, LLM fine tuning, and re-evaluating (without multi-year contracts).
I used Gundam mode for dense diagrams and saw roughly thirty percent better layout fidelity. Fine tuning on a tiny domain set helped more than I expected. Fifty invoices and loan forms cut error rates nearly in half.
DeepSeek OCR: How to Use for Text Extraction Tasks
Deployment methods and complexity
DeepSeek OCR vLLM (officially supported):
- Requires: CUDA 11.8+, PyTorch 2.6.0, Flash Attention 2.7.3, 16GB+ VRAM
- Community feedback: Complex setup with frequent dependency conflicts
- Best for: Production deployments with GPU infrastructure
Transformers:
- Simpler installation, slower inference
- Suitable for: Batch processing, prototyping
Third-party DeepSeek OCR API options:
- Clarifai, Deep Infra, Simplismart
- Zero setup, per-request pricing
- Trade-off: Vendor dependency, cost at scale
Production deployment gaps
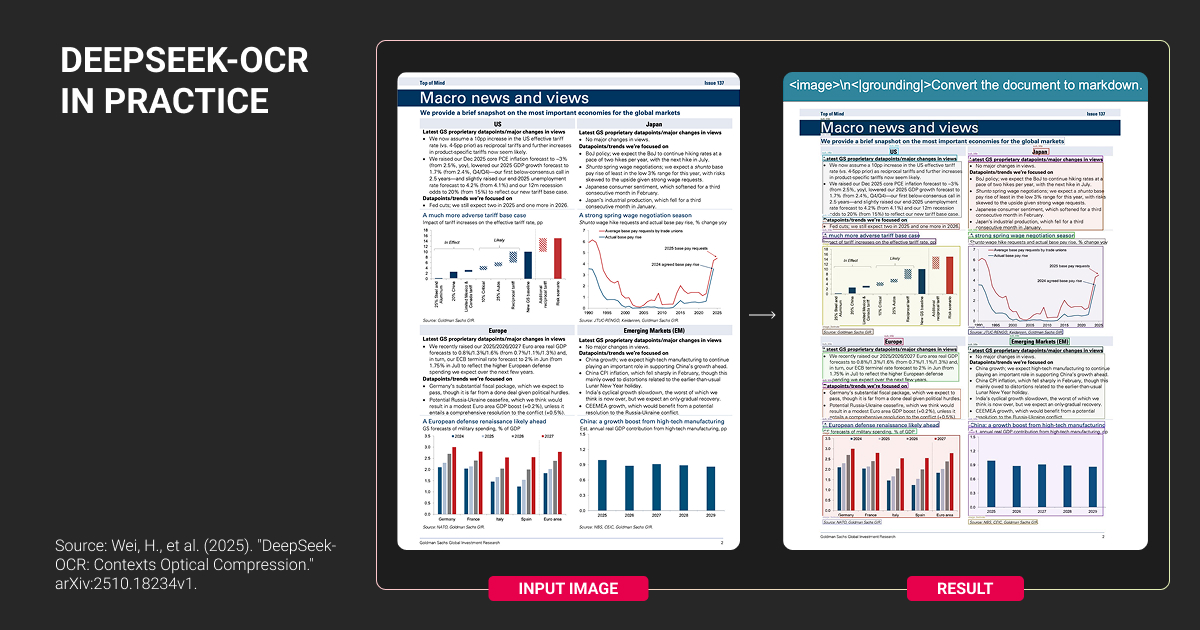
Prompt sensitivity: Exact formatting required—missing punctuation causes complete failure:
- Layout mode: <image>\n<|grounding|>Convert document to markdown. (period required)
- Plain text: <image>\nFree OCR. (period required)
- Missing newline/period = unpredictable output
Hardware constraints:
- 16GB VRAM minimum (eliminates consumer GPUs)
- CPU-only: 10-50x slower than GPU
- 10-14GB typical consumption
Multilingual processing: “Significantly slower than single-language tasks” — suggests training imbalance (25M English/Chinese pages, 5M across 75+ languages).
No native PDF support: Requires preprocessing (100-500ms per page), adding latency and complexity.
Consult DeepSeek OCR API documentation for exact prompt formatting requirements, as missing punctuation causes complete failures.
Training data improves deployment robustness
Models trained on varied conditions exhibit production resilience. Training needs:
- Multiple resolutions (512×512 through 1280×1280 + intermediates)
- Compression artifacts (JPEG quality variations)
- Preprocessing variations (with/without deskewing, binarization)
Current prompt sensitivity indicates training used standardized prompts exclusively. Tool-agnostic annotation enables testing vLLM vs. Transformers vs. APIs with the same training data, reducing production risk before infrastructure commitment.
Explore production-ready OCR algorithms for automating document processing workflows.
DeepSeek OCR vs Traditional OCR: Performance Comparison
Benchmark performance comparison
| Model | Tokens/Page | Edit Distance | Key Advantage |
| DeepSeek Small | 100 | 0.221 | Token efficiency |
| GOT-OCR2.0 | 256 | 0.287 | - |
| DeepSeek Gundam | 795 | 0.127 | Best end-to-end |
| MinerU2.0 | 6,790 | 0.133 | Layout preservation |
Token efficiency winner: DeepSeek achieves 8.5x fewer tokens than MinerU for equivalent benchmark accuracy.
Production reality diverges: MinerU maintains 90.67 layout preservation on complex documents where DeepSeek degrades to 75-80 range. Traditional pipelines win on financial statements, regulatory filings, and dense tables.
Why specialized models sometimes win
Traditional OCR pipelines use task-specific training:
- Layout detection model: 50,000 documents with layout annotations
- Table extraction model: 30,000 tables (10K financial, 10K scientific, 10K forms)
- Text recognition model: Millions of text images
DeepSeek OCR model learns all tasks simultaneously from mixed data. If financial tables represent 5% of training (1.5M of 30M pages), table extraction becomes secondary versus primary skill.
Mathematical reality: Dedicated table model trained on 30,000 diverse tables outperforms general OCR trained on 30M documents where tables are incidental.
Optimal deployment strategy: hybrid architecture
Simple documents → DeepSeek:
- Forms, books, correspondence (95-98% accuracy, 100-256 tokens)
Complex tables → MinerU/specialized pipelines:
- Financial statements, technical specs (90-95% accuracy, 6,000+ tokens, justified by requirements)
Low confidence → Human review:
- Handwritten, degraded scans (99%+ accuracy required)
Hybrid approach achieves 95-98% system accuracy while optimizing token consumption. Implication: teams need a data annotation company or a data annotation platform covering the full document complexity spectrum for accurate upstream classification and targeted model selection.
What Production DeepSeek-OCR Deployment Actually Requires
DeepSeek OCR’s 97% benchmark accuracy assumes standardized documents. Production environments don't cooperate.
Start with document analysis, not infrastructure
Run a 100-document sample through DeepSeek before committing to deployment. Split it: 20% clean PDFs, 80% real-world chaos (watermarks, degraded scans, dense tables, mixed layouts). If accuracy drops >15% on the messy majority, architecture won’t fix it — training data will.
Calculate token distribution across your documents. DeepSeek performs best at 512-1024 tokens. Financial statements average 1,200-1,800 tokens. Newspapers hit 795+ tokens. Dense technical specs exceed 2,000 tokens. If your documents consistently push past 1,200 tokens, you're operating in DeepSeek's degradation zone (60% accuracy at 20x compression).
Test domain-specific accuracy separately. General benchmarks don’t predict financial statement performance or medical record accuracy. Run your actual document types. Production teams report 75-80% accuracy on SEC filings versus 95%+ benchmark claims. That 15-20% gap represents missing domain expertise in training data.
Plan annotation needs based on failure analysis
- Edge cases causing 60-80% of errors need 500-1,000 targeted examples
- Domain-specific documents need 1,000-2,000 examples matching production distribution
- Multilingual requires native speaker validation, not machine translation
Hybrid architecture beats single-model deployment. Document classification routes simple documents to DeepSeek (token efficiency), complex layouts to specialized pipelines (layout preservation), low-confidence outputs to human review (accuracy requirements). Upstream classification needs training data spanning the full document complexity spectrum.
What I appreciate most is that DeepSeek OCR feels like it’s built for the documents we actually encounter, not the perfectly aligned PDFs most models are benchmarked on. It's not flawless, but in real business workflows where speed and correction cost matter, it's become the tool I default to first.
Teams deploying DeepSeek OCR model need expert and secure annotation strategies addressing real-world document diversity to close the benchmark-to-production gap.
About Label Your Data
If you choose to delegate data annotation for OCR models, run a free data pilot with Label Your Data. Our outsourcing strategy has helped many companies scale their ML projects. Here’s why:
Check our performance based on a free trial
Pay per labeled object or per annotation hour
Working with every annotation tool, even your custom tools
Work with a data-certified vendor: PCI DSS Level 1, ISO:2700, GDPR, CCPA
FAQ
Does DeepSeek have OCR?
Yes. DeepSeek released DeepSeek-VL2, a vision-language model with native OCR capabilities. It processes document images and extracts text in 100+ languages, supporting both plain text extraction and structured markdown conversion with layout preservation.
How to use DeepSeek OCR?
- Install vLLM with CUDA 11.8+, PyTorch 2.6.0, and Flash Attention 2.7.3
- Load deepseek-ai/deepseek-vl2 model from DeepSeek-OCR Hugging Face model card
- Format prompts with exact syntax (missing punctuation causes failures)
- Requires minimum 16GB VRAM GPU for processing
- Alternative: Use third-party DeepSeek OCR API options: (Clarifai, Deep Infra, Simplismart) for zero-setup deployment
How accurate is DeepSeek-OCR?
DeepSeek achieves 97% accuracy on standardized benchmarks at 10x compression ratios. Production accuracy varies by document type: 95-98% on clean forms and correspondence, 75-80% on complex financial documents with dense tables, 60% accuracy when compression exceeds 20x ratio. Accuracy degrades 15-25% on documents outside training distribution (watermarked scans, unusual layouts, domain-specific formats).
What hardware is needed for DeepSeek OCR?
Minimum: 16GB VRAM GPU (eliminates consumer-grade GPUs like RTX 3060). Recommended: A100 or H100 for production throughput (200,000+ pages per day per GPU). Typical consumption: 10-14GB VRAM during inference. CPU-only deployment is possible but runs 10-50x slower than GPU, making it impractical for production volumes.
Can DeepSeek-OCR run on CPU?
Yes, but not recommended for production. CPU inference runs 10-50x slower than GPU deployment. A document processing 2 seconds on GPU takes 20-100 seconds on CPU. Suitable only for prototyping or extremely low-volume scenarios (single-digit documents per hour). Production deployments require GPU infrastructure.
Is DeepSeek API free?
No. DeepSeek API uses pay-as-you-go pricing: $0.07-$0.27 per million input tokens, $1.10 per million output tokens (deepseek-chat rates). The free web chat at chat.deepseek.com does not include API access. For production OCR, budget for API costs or self-host the open-source model (MIT license) to eliminate API charges.
Written by
Karyna is the CEO of Label Your Data, a company specializing in data labeling solutions for machine learning projects. With a strong background in machine learning, she frequently collaborates with editors to share her expertise through articles, whitepapers, and presentations.




