Artificial Intelligence in the New Media Industry

The initial purpose of the media was to inform, educate, or entertain the public via a handful of media outlets. It was a different way to communicate and impact society in general. However, such focus has shifted today, with artificial intelligence laying the groundwork for the new media era.
A little while ago, we discussed how AI has redefined the modern approach to content moderation. More specifically, the issue we’ve covered was how to use AI for responsible social media management, since it significantly affects the life of a modern user. But what if we take a look at the media sector as a whole and examine the impact artificial intelligence has on it today?
The media sources find us everywhere, from personal devices to streets and public places. This means that the media has a much more tangible and inevitable influence on modern-day society than we used to think. Hence, AI should be trained to become a valuable asset that takes control over this influence and keeps the media safe and useful for us.
You’ve probably heard of the case when AI wrote its first article for The Guardian, all by itself, using a GPT-3 model. Here, AI declares itself loudly through the title of this article, so should we be worried? Should we question AI-generated media?
We’ll answer these questions throughout this article, so stay tuned! Label Your Data puts AI under the microscope of the media world!
AI Applications in the Media & Entertainment Sector

The main idea behind implementing artificial intelligence in the media and entertainment sector is to increase the interactivity and appeal of visual material. Hence, the visual media is more engaging and dynamic when combined with smart tech solutions. Also, AI enables automated and data-rich media content that, in turn, delivers a more personalized and entertaining viewer experience. For example, automated article classification is gaining traction among media providers due to the tough competition in the industry.
However, modern media creators and enterprises struggle to create material in large quantities while maintaining quality, which is why they turn to AI to accomplish this goal. AI businesses are continuously attempting to improve the efficiency of the entertainment industry by integrating this technology into a variety of sub-fields. AI applications in media and entertainment are expanding quickly, particularly when it comes to sharing and displaying visual content.
What are these AI applications in the major media industries? Let’s find out!
Music
DL generative models are used to handle advanced audio features (e.g., timbre). AI is also applied for style transfer, audio demixing, and personalized music production. Not without personalized recommendations in the music scene, customized content, and enhanced playback to allow users to control the sound.
The main challenges for AI in this area include models that use raw audio signal information, learning long-term temporal dependencies, switching between timbres, as well as denoising and demixing.
Visual Arts
Applications for AI-generated art images, pastiches, and images from captions are among the key AI applications in visual arts. Additionally, AI can be used for reproducing scene-dependent image transformations, style-based image transformations, image inpainting, image retrieval based on text or visual features, and image quality improvement. AI solutions in this sector imply automatic metadata creation based on the analysis of the image or text, as well as object detection and face recognition algorithms.
The challenges that AI encounters while working with the images include cross-media search, learning to understand image content, image generation from the description, and automated reconstruction of the missing elements.
Digital Storytelling
AI-powered cinematography, transmedia storytelling, authoring tools for non-experts, sensor-based storytelling for immersive experiences, and searching archives to discover content that best fits the narrative are all part of innovative digital storytelling with the help of AI. Audio segmentation and multimodal interactive and virtual experiences are enabled due to AI within the content production stage.
However, there are some throwbacks to consider, such as automated narration in an interactive environment and transdisciplinary storytelling that merges writing, tech, and gaming. Also, authors must retain control over the AI-generated content.
Games, Movies, Engineering, and Design
In these particular industries, AI enables automated content synthesis, by-example synthesis, and generative game design. As a result, users benefit from personalized games that are adjusted to gamer profiles and AI’s ability to model the player’s behavior, skills, and affective state.
Here, the current difficulties include the synthesis of large environments, ethics by design to avoid addiction, and credible assessment of the user’s emotional state.
Book Publishing
AI greatly relieves the publication process by automating all the work for the publishing houses. Additionally, publication tagging, personalized book recommendations, and copyright management are much enhanced due to AI. It also helps improve the accessibility for people with print impairments (e.g., automated text generation to describe a specific image). Yet, the IPR issues must be thoroughly addressed, considering AI input and output.
Media Access Services
AI solutions for this sector encompass sign language production (SLP), audio description of the content, and automatic subtitling (multilingual, contextualized, and in accordance with legislation).
However, the most prevalent challenges, in this case, are automated multilingual translation and optimization of the audio-visual content circulation through translation.
News
AI became a powerful tool for the news media over recent years, given that it facilitates fact-checking as well as analysis and cross-examination of information sources (in different languages). The technology also powers content verification (e.g., deep fakes detection), social network analysis (disinformation detection), and automated generation of personalized news digests. All this is feasible thanks to user profiling and ML-based recommender systems, smart solutions for evaluating the credibility of the information in the news, and tools for better quality participative journalism. Automated news aggregation and summarization also come into play in the AI-driven news media industry.
Nonetheless, the main concerns in the news sector are the transparency and reliability of AI algorithms, heterogeneous data integration and search, as well as security and privacy issues of multimodal information retrieval systems and video forensics.
Social Media
As we’ve already discussed in one of the previous articles, AI for social media is mainly used to enable content personalization, develop recommender systems, enhanced content search and moderation, ad placement, and trend identification. AI is also a useful approach to opinion mining (aka sentiment analysis) for more in-depth social media analysis.
AI in Journalism: Entering the Era of Synthetic Media
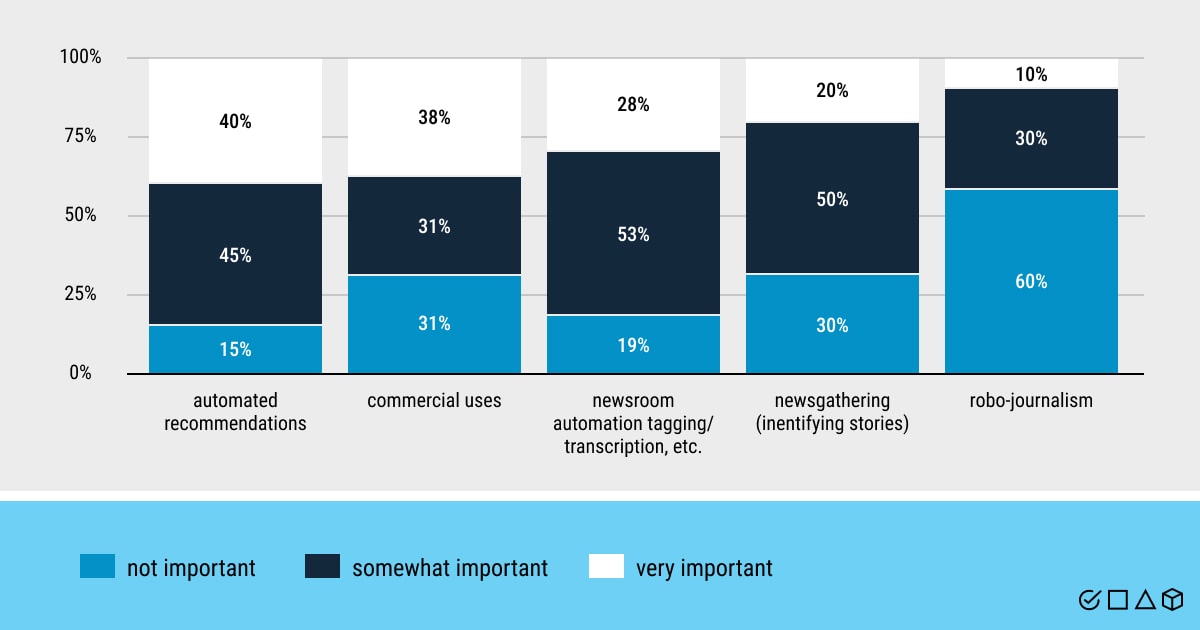
It looks like artificial intelligence is setting a new course in the media realm, with technical progress on the rise. However, the immature nature of AI in this field makes the experts (i.e., journalists and other contributors) question the reliability and usefulness that AI may bring to the table. Other important issues are the challenges that might occur once AI has been integrated into the complex media pipeline. More specifically, how smoothly machines can blend with journalism, communication, stories, and human passion for the written word.
While some doubt the effectiveness of AI-driven journalism these days, other professionals think of AI as a way to conquer new horizons of innovative, high-quality journalism and media as a whole. As a result, journalists would be able to forget about repetitive, routine, and tiresome tasks, and focus on the creative side of the media content instead. This is how AI is expected to add value to the journalistic field.
Artificial intelligence presents a wide range of opportunities for enhancing and complementing the tedious work of information professionals. Although AI is being employed in many newsrooms, one of the true goals is to achieve augmented journalism by taking full advantage of automation. What are these benefits that artificial intelligence has brought to journalists?
With a mindful use of AI-powered tech, journalists can accomplish the following tasks with ease:
- Recognize and identify patterns, trends, and ideas from multiple sources;
- See things that the human eye is unable to perceive;
- Automatically convert data and words into the text;
- Translate text into audio and video automatically;
- Analyze and comprehend user behaviors;
- Analyze scenes from objects.
AI journalism refers to the automated production of news articles by computers as opposed to human reporters. The news is translated, arranged, and presented in a human-readable manner thanks to this technology. Artificial intelligence uses algorithms to process mass volumes of data, choose among pre-programmed article formats, insert necessary information (such as names, statistics, and figures), and put key points.
In light of the development of AI in this media industry, the advanced practices of tech-oriented journalism have gone viral, such as:
- Data Journalism
An increasingly large quantity of numerical data is used to produce news stories in data journalism, which is a more recent kind of journalism, and makes them simpler for the audience to grasp. Data journalism helps the public comprehend the intricate ideas employed in AI-generated news articles.
- Algorithm Journalism
Another emerging format of journalism is algorithm journalism, which employs digital processing at the point where journalism and data technology converge. Additionally, the method relies heavily on a combination of algorithms, data, and knowledge to raise the credibility of the journalistic work.
- Automated Journalism
Automated journalism is the production and automatic distribution of a greater amount of news information for the consumption of audiences. The data collection may be transformed into news stories using an algorithm approach for readability and human interest.
Key Benefits of AI-Driven Journalism
- Personalized content. Personalization is a tactic that news publishers use to boost user engagement on their websites and collect user data to lessen their reliance on external information sources.
- News detection. AI is capable of monitoring hundreds of sources or identifying breaking news by keywords through data collection, categorization, selection according to categories, and structural grouping.
- Debunking misinformation.Deep fakes are common, and AI capabilities are often being used unlawfully, which has brought attention to the need for media literacy, helping people to be educated, involved, and motivated to think critically.
- Automated generation of journalistic content.This is a trend in media outlets that have chosen to use AI to enhance their information offering and boost performance.
Data Annotation for Media Projects in AI

For any AI application to succeed, the dataset must be accurately annotated. Even while the most efficient AI algorithms still rely on data labeling and ground truth, genuinely creative processes sometimes lack a mechanism to assess the quality of the output in advance. Labeling is, in any event, a viable strategy for assuring the reliable implementation of AI in the media sector.
In case you work in a different sector from media and have a model to train, send your data to us, so we can annotate it and help you succeed with your AI project underway! By the way, the pilot project is free, so don’t hesitate to contact Label Your Data!
Now, let’s talk about real-life examples of AI applications in the media and appropriate data annotation methods for each!
- Face Recognition
When reporting on or covering significant global issues, the media may effectively make use of face recognition systems to identify the many types of faces captured in the photographs or videos. The data annotation methods used here are landmark annotation and semantic segmentation.
- Brand Recognition
The media sector employs ML models to identify well-known companies, their names, logos, and tags, so that they can be identified when recording movies or taking photos (at random). These brand names may be annotated using bounding boxes or polygons, which makes it simpler for AI to recognize them in a crowd and alert the media person.
- Visual Search
Visual search technology is essential for identifying objects in a photo frame while reporting on a certain story or topic. When an ML model is trained to recognize target objects (i.e., object detection for images and object tracking for videos), it becomes simpler for the machine to notice them when they are recognized by computer vision. Annotated datasets must be accurately constructed to train the visual search algorithms.
- Sentiment Analysis and Language Processing
Text annotation is a common technique used for sentiment analysis and language processing tasks. This way, labeled data helps machines make sense of textual information. To make the full phrase or text easily understood using language-based ML training, the keywords are annotated with additional metadata, keynotes, and other tags.
- Fake News Detection
The fake news, provided by untrustworthy sources misleading the public, may be identified by news or media agencies with the help of NLP labeling (natural language processing). In fact, when annotated language is used to train AI models, they learn to recognize certain types of bogus news and report others.
- Entity Extraction
Named entity recognition, or simply NER annotation, is used to identify popular names for entities and the connections between them. By correctly extracting these names and associated entities from documents using an ML model, the news and media sector can witness significant improvements and increased efficiency in their work.
Summary: The Future of Media is Data-Driven, What’s Next?

More sophisticated and intelligent approaches to effect control are required as the media industry increases its influence on the public mindset and society at large.
The era of creating and modifying material solely in analog and digital formats is coming to an end. Hence, the long-established methods for contributing to and creating media content, as well as the public’s view of it, are all being fundamentally altered by AI. Synthetic media is gaining ground quickly, and we will see more and more AI applications in this sector that will test our sense of reality and test our grasp of what is true and false.
We can see how data annotation is essential to guarantee that AI is applied effectively and produces accurate and reliable results, which bodes well for the future of AI in media. To stop the spread of disinformation and the hazardous impact of the media, it’s crucial to make AI an asset rather than a liability when it comes to recognizing fake content (i.e., news, deep fakes).
Having said that, we cannot create the most responsible media without using AI carefully and maintaining our own capacity for critical thought. And if you need a hand with expert data annotation, contact our Label Your Data team so that your AI project is destined to succeed!
Written by
Karyna is the CEO of Label Your Data, a company specializing in data labeling solutions for machine learning projects. With a strong background in machine learning, she frequently collaborates with editors to share her expertise through articles, whitepapers, and presentations.

