Best Image Segmentation Models for ML Engineers
Table of Contents
- TL;DR
- Image Segmentation Models in 2026: What Changed for ML Teams
-
How to Choose Among the Best Image Segmentation Models
- SAM 3: Foundation model for promptable segmentation
- Mask2Former: Transformer for panoptic segmentation
- DeepLabV3+: CNN baseline for semantic segmentation
- Mask R-CNN for classic instance segmentation
- U-Net and nnU-Net for medical imaging specialists
- HRNetV2+OCR for high-resolution semantic segmentation
- YOLACT++ for real-time instance segmentation
- Training Considerations for Image Segmentation Models
- Label Your Data’s Approach to Image Segmentation Annotation
- Best Image Segmentation Models Comparison
- Choosing the Best Image Segmentation Model for Your ML Project
- About Label Your Data
- FAQ

TL;DR
- SAM 3’s real value is auto-labeling datasets, not production inference; foundation models still need domain-specific fine-tuning despite zero-shot claims.
- Classic architectures like Mask R-CNN and nnU-Net remain production workhorses because specialized models outperform newer transformers in their domains.
- Annotation quality determines model performance more than architecture choice; boundary precision and consistent guidelines matter more than picking the latest model.
You're three weeks into training a segmentation model, but the validation metrics look wrong.
Here's what benchmark comparisons won't tell you: SAM 3 runs 55× slower than YOLO11 for comparable tasks, yet nnU-Net still outperforms transformer variants in medical imaging when properly controlled.
The image segmentation models landscape in 2026 spans from foundation models processing 270K+ concepts to real-time systems hitting 33 FPS, but selecting the wrong model wastes weeks of compute and thousands in data annotation pricing.
This guide covers the best image segmentation models with real-world benchmarks, hardware requirements, and insights from ML engineers who've deployed them in production.
Image Segmentation Models in 2026: What Changed for ML Teams
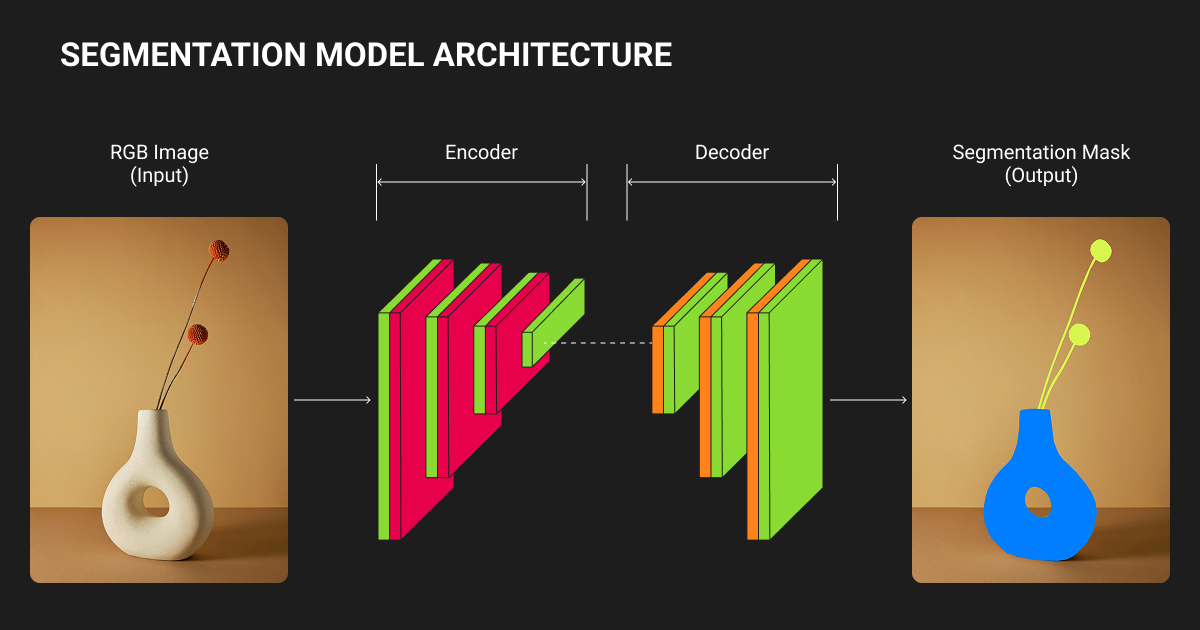
Foundation models enter production
Meta's SAM 3, released November 2025, introduced text-prompt capabilities that earlier versions lacked. You can now segment "all yellow school buses" using natural language instead of geometric prompts.
The model handles 270,000+ unique concepts in zero-shot settings, achieving 48.5 AP on LVIS versus the previous best of 38.5.
If you've been following foundation model evaluations, you've probably noticed something off about the benchmarks. I recently analyzed Medical SAM3's performance and found that its "universal" capabilities relied on ground-truth bounding boxes at inference. With text-only prompts, performance dropped to 11.9% Dice before domain fine-tuning.
Yet, practitioners discovered SAM 3's real value isn't inference deployment. As one ML engineer noted: "The killer app for SAM 3 isn't running it in production—it's using it to label data."
The model runs at ~30ms per image on H200 GPUs with 8GB VRAM, but it's 55× slower than YOLO11. The trade-off is 12× superior boundary stability.
Transformers overtake CNNs for complex tasks
Mask2Former achieved SOTA across panoptic, instance, and semantic segmentation: 57.8 PQ on COCO panoptic with a Swin-L backbone. It introduced masked attention, enabling 8× faster convergence than Mask R-CNN.
If you're working on autonomous driving, robotics, or advanced image recognition systems where you need both semantic context and instance separation, this matters.
Training requires 15+ GB VRAM minimum; Swin-L configurations demand 32+ GB. Inference runs at 8.6 FPS on V100, dropping to ~2 FPS on edge deployment. You'll need pre-trained weights because training from scratch performs poorly.
Specialization still matters
nnU-Net won 9 out of 10 MICCAI 2020 challenges without manual tuning.
A 2024 benchmark concluded transformer architectures like SwinUNETR failed to match CNN baselines when properly controlled. If you're working with medical imaging and 100-500 training scans, nnU-Net's automatic configuration outweighs theoretical architectural advantages of newer models.
Sometimes the older approach just works better for your domain.
How to Choose Among the Best Image Segmentation Models
Here's your decision framework based on what you're actually building:
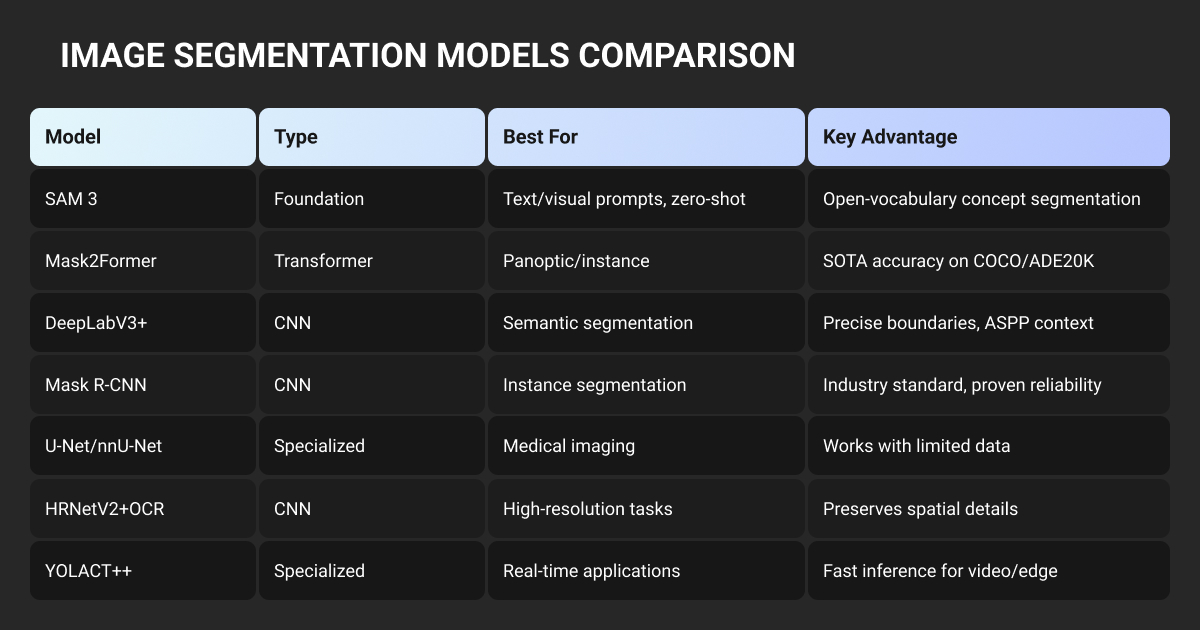
| Your Need | Model | Why |
| Zero-shot / no training data | SAM 3 | Text prompts, 270K+ concepts |
| Panoptic segmentation | Mask2Former | 57.8 PQ COCO after fine-tuning |
| Semantic baseline | DeepLabV3+ | Proven CNN, 8GB VRAM |
| Instance precision | Mask R-CNN | 43K citations, best for overlap |
| Medical imaging | nnU-Net | 90%+ Dice, auto-configures |
| High-resolution | HRNetV2+OCR | 84.5% Cityscapes |
| Real-time | YOLACT++ | 33 FPS, 1.5GB VRAM |
Consider your infrastructure: transformers need more VRAM than CNNs. Foundation models reduce labeling needs, but fine-tuning improves accuracy 5-15% for specialized tasks. Test on your domain; COCO benchmarks may not reflect your data distribution.
SAM 3: Foundation model for promptable segmentation
SAM 3 segments objects using text or visual prompts without task-specific training. The architecture comprises 848 million parameters with a Presence Token that predicts whether a concept exists before localizing it, achieving 2× performance gains.
If you're prototyping quickly or working with datasets under 500 images, SAM 3's zero-shot capabilities let you skip the initial data annotation phase. It reaches 75-80% of human performance on the SA-Co benchmark and handles ambiguous prompts reasonably well.
But here’s the catch: it's 55× slower than YOLO11 for comparable tasks. You're trading speed for 12× superior boundary stability. It struggles with complex reasoning and needs fine-tuning for niche domains. Large model size requires 8GB+ VRAM.
Use for auto-labeling datasets, rapid prototyping, and edge cases where retraining isn't practical. Requires Python 3.12+, PyTorch 2.7+, and CUDA 12.6+. Works with HuggingFace, Ultralytics, Roboflow, CVAT, and other data annotation tools.
When our model missed tricky classes, quick iterations were key. We'd pinpoint the exact scenes the model messed up, fix the labels, and retrain right away. Do small batch fixes instead of re-labeling everything at once—you learn faster and don't burn out your team.
Mask2Former: Transformer for panoptic segmentation
Single transformer architecture handling semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation. Masked attention constrains cross-attention to predicted mask regions. Point sampling reduces GPU memory by 3×.
You'll get 57.8 PQ on COCO panoptic, 8× faster convergence than Mask R-CNN, and excellent boundary quality. Reddit's community calls out its "very precise mask borderline" due to positional embeddings that help with object relations across resolutions.
Budget for 15-32GB VRAM during training. Pre-trained weights are essential, so skip the from-scratch approach. Inference runs at 8.6 FPS on V100, which drops to ~2 FPS on edge devices. You're looking at higher-quality masks at the cost of speed and memory.
Use for autonomous driving or robotics where you need both semantic and instance outputs. Available via Detectron2 and HuggingFace. However, note that OneFormer now offers better single-training universality if that's your goal.
DeepLabV3+: CNN baseline for semantic segmentation
Google's ASPP-based encoder-decoder that achieves 87.8% mIoU PASCAL VOC, and 82.1% Cityscapes with an Xception backbone.
If you're setting up a semantic segmentation baseline or working with resource constraints, this is where you start.
8GB VRAM sufficient, converges in 20-30 epochs, and has extensive framework support (PyTorch, TensorFlow, MATLAB, MMSegmentation). Many ML practitioners still use it as the CNN baseline for comparisons (that tells you something about its reliability).
Lower accuracy than transformers on complex scenes, cannot handle instance segmentation, and IoU drops 10-15% for objects under 32px. Requires batch size ≥12 for effective batch norm training. Training takes ~13 hours on 2× 1080Ti for Cityscapes.
Use for semantic segmentation baselines, resource-constrained scenarios with MobileNet backbone, when transformer overhead isn't justified by your accuracy requirements.
Mask R-CNN for classic instance segmentation
Two-stage architecture extending Faster R-CNN with mask prediction. RoIAlign eliminates spatial misalignment, causing 10-50% accuracy degradation.
This is the industry standard for good reason. Works with 1,000-5,000 labeled data instances, superior for overlapping objects requiring precise pixel-level segmentation. If accuracy matters more than speed for your use case, you're probably ending up here.
It's 5-7 PQ points below transformers on panoptic tasks, runs at ~5 FPS, and requires NMS post-processing. YOLOv8 achieves 0.90 precision/0.95 recall versus Mask R-CNN's 0.81/0.81 on agricultural datasets. You're paying for precision with slower inference.
Use for complex scenes with overlapping objects where accuracy is non-negotiable. Training requires multiple V100 GPUs. Fine-tuning from COCO weights is fast with pre-trained checkpoints. Available in Detectron2, MMDetection, and TorchVision.
U-Net and nnU-Net for medical imaging specialists
U-Net works with as few as 30 training images. nnU-Net, instead, automates the entire pipeline: preprocessing, architecture, hyperparameters, and inference.
If you're working in medical imaging, these are the default medical image segmentation models. nnU-Net won 9/10 MICCAI 2020 challenges and 5/7 MICCAI 2021 challenges without manual tuning. 90%+ Dice on medical benchmarks.
The 2024 benchmark finding that transformers fail to match CNN performance when properly controlled makes this recommendation even stronger.
Works with 100-500 annotated scans through automatic configuration. Not designed for natural images (underperforms on COCO/ADE20K), 3D nnU-Net requires 24-32GB VRAM, limited to semantic segmentation, not FDA-cleared as-is.
Use for medical imaging (CT, MRI, histopathology) or 3D volumetric data. Hardware: minimum RTX 2080 Ti (11GB), recommended RTX 3090/4090 or A100. Training: under 2 days on RTX 2080 Ti.
HRNetV2+OCR for high-resolution semantic segmentation
Maintains high resolution throughout via parallel multi-resolution branches, achieving 84.5% mIoU on Cityscapes with SegFix post-processing.
Best for fine spatial detail work like satellite imagery, fashion parsing, or anything where you need to preserve small object boundaries. It achieves 81.6% mIoU on Cityscapes validation, which is 2-3 points above DeepLabV3+ on ADE20K.
SegFormer-B5 now achieves 51.8% ADE20K with 27.5M parameters versus HRNet's 70.5M. Multi-branch operations hinder hardware acceleration. Training HRNet-W32 takes ~50-60 hours with 4 P100 GPUs.
You're getting better spatial precision at the cost of efficiency.
Use for position-sensitive tasks (pose estimation, medical imaging) requiring precise spatial localization. Frameworks: MMSegmentation, timm, MMPose, PaddleSeg.
YOLACT++ for real-time instance segmentation
Single-stage model achieving 34.1 mAP at 33.5 FPS. It breaks segmentation into parallel tasks: generating 32 prototype masks and predicting per-instance coefficients.
If you need real-time performance, this is your entry point.
1,500 MB VRAM only, 172.7 FPS on RTX 2080 Ti with TensorRT, 30.8 FPS on Jetson AGX Xavier. Better temporal stability in videos than Mask R-CNN (masks don't jitter when objects are stationary). The architecture influenced YOLOv8 segmentation, which tells you it got something fundamentally right.
Mask leakage when bounding boxes are inaccurate, struggles with dense overlapping objects, 5-6 AP points below Mask2Former, and weaker small object performance. Here, you're trading accuracy for speed.
Use for video segmentation, robotics, AR/VR, or edge deployment where latency under 30ms is required. Note that RTMDet-Ins is the current SOTA real-time alternative (52.8% AP, 300+ FPS RTX 3090).
Run inference on a validation set to collect failures based on class, size, and occlusion. Prioritize hard negatives, rare instances, and boundary-heavy examples. End every cycle with class-specific metric review—if one class stagnates while others improve, don't move forward. Iteration speed and annotation precision matter more than dataset size.
Training Considerations for Image Segmentation Models
Fine-tuning vs. training from scratch
Foundation models like SAM 3 work zero-shot but improve 8-15% mIoU with fine-tuning. Use SAM 3 zero-shot if your annotation budget is under 500 images. Fine-tune DeepLabV3+ or Mask R-CNN for most production cases involving machine learning model training.
Data requirements:
- Transformers: 50K-100K masks, 100-200 epochs
- CNNs: 5K-20K masks, 30-50 epochs
- Medical nnU-Net: 100-500 scans
- SAM 3 adapter: 200-1K masks
At this scale, partnering with a trusted and GDPR-compliant data annotation company that can handle batch workflows and maintain quality control becomes essential for most ML teams.
Normalization layers impact production reliability
Normalization choices matter more than most architecture papers acknowledge.
Research on image segmentation models shows group normalization enhances robustness to blur, noise, and weather corruptions. Batch normalization improves generalization across different machine learning datasets where feature statistics change.
If your model encounters varying input conditions in production, such as different cameras, lighting, or weather, your normalization choice affects reliability as much as your architecture.
Label Your Data’s Approach to Image Segmentation Annotation
Boundary precision beats dataset size every time. Case in point, when Nexvision needed ellipse-level precision for 40,000 pupil images to train gaze detection models, automated tools couldn't deliver.
We at Label Your Data ran three parallel workflows over 6 months: pupil segmentation with precise ellipse masks, eye detection with bounding boxes, and maritime object tracking across 4,000 videos. Zero quality escalations, all batches on time.
AirSeed Technologies faced a different challenge: training drones to plant trees on degraded land. They needed polygon-labeled maps across 50+ large geofiles where the difference between plantable zones and rocky outcrops directly impacts model accuracy.
Our 6-person team delivered 30+ ML-ready maps in 5 months, fitting their stack without cleanup. As their VP of Engineering noted: "The [Label Your Data] workflow was smooth, progress was steady, and the quality consistently met our expectations."
Here's what both cases proved: your image segmentation model choice matters, but inconsistent annotation guidelines kill convergence faster than picking the wrong architecture. This is where professional data annotation services make the difference.
When our AI kept getting the same things wrong, we worked directly with annotators to retrain it on those specific objects. After we added quick check-ins after each batch, the recurring errors fell off fast. Check in after every major batch—you catch issues early.
Best Image Segmentation Models Comparison
| Model | Primary Use Case | COCO/Best Benchmark | Speed (FPS) | GPU Memory | Production Readiness |
| SAM 3 | Open-vocabulary segmentation | 48.5 AP (LVIS) | ~30ms (H200) | 8GB+ | Auto-labeling recommended |
| Mask2Former | Universal segmentation | 57.8 PQ (COCO) | 8.6 | 15GB+ | Research/cloud |
| DeepLabV3+ | Semantic segmentation baseline | 87.8% (VOC) | ~20 | 8-12GB | Production-proven |
| Mask R-CNN | Precise instance segmentation | 35.7 AP (COCO) | ~5 | 6-12GB | Production-proven |
| nnU-Net | Medical imaging | 90%+ Dice | Varies | 10GB+ | Research (FDA path needed) |
| HRNetV2+OCR | High-resolution semantic | 84.5% (Cityscapes) | ~24 | 8-16GB | Production-ready |
| YOLACT++ | Real-time instance | 34.1 AP (COCO) | 33.5 | 1.5GB | Edge-deployable |
Choosing the Best Image Segmentation Model for Your ML Project
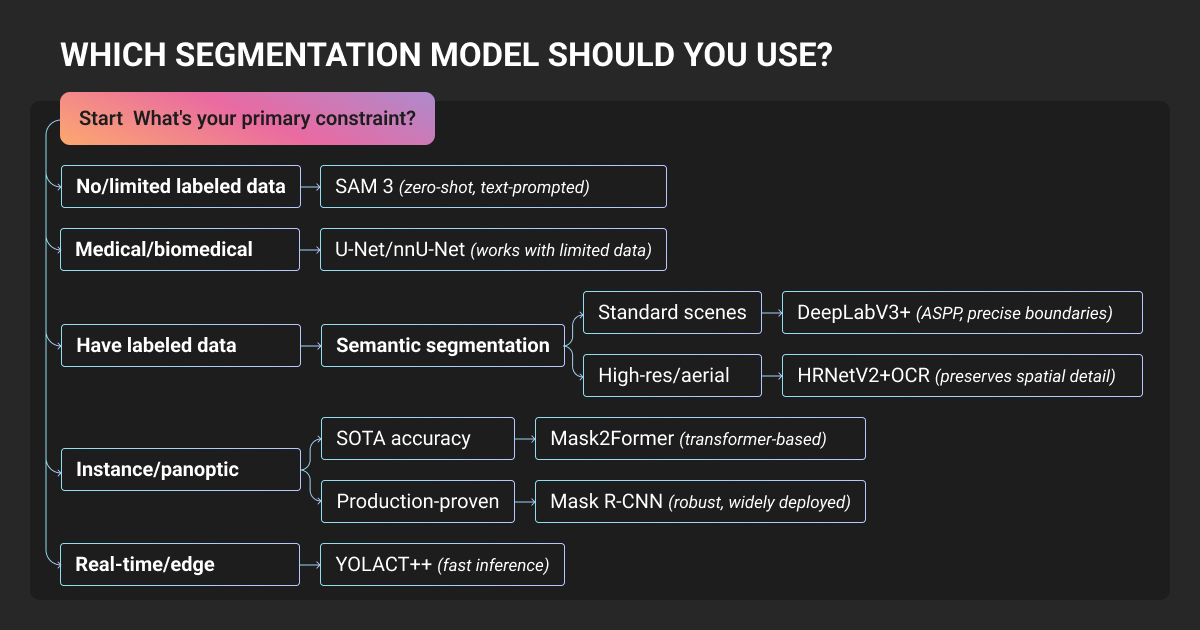
No single model dominates all use cases.
Classic architectures remain production workhorses: Mask R-CNN and nnU-Net continue proving "old" doesn't mean obsolete when accuracy requirements exceed real-time constraints. Each machine learning algorithm has trade-offs between speed, accuracy, and domain specialization.
Transformer hype requires scrutiny; rigorous benchmarks show CNN U-Nets outperforming transformer variants when properly controlled.
Start with the simplest model meeting your requirements:
- Semantic segmentation baseline: DeepLabV3+ (proven stability, extensive framework support)
- Medical imaging: nnU-Net (auto-configures, transformers fail to match CNN performance)
- Real-time applications: YOLACT++ or YOLOv8-seg (edge-deployable, 33+ FPS)
- Maximum accuracy: Mask2Former (only when complexity is justified)
- Dataset creation: SAM 3 (open-vocabulary auto-labeling workflows)
Need high-quality segmentation annotations to train or fine-tune these models? Label Your Data provides pixel-accurate segmentation labeling with domain experts across 16 countries.
About Label Your Data
If you choose to delegate image labeling for segmentation models, run a free data pilot with Label Your Data. Our outsourcing strategy has helped many companies scale their ML projects. Here’s why:
Check our performance based on a free trial
Pay per labeled object or per annotation hour
Working with every annotation tool, even your custom tools
Work with a data-certified vendor: PCI DSS Level 1, ISO:2700, GDPR, CCPA
FAQ
What are segmentation models?
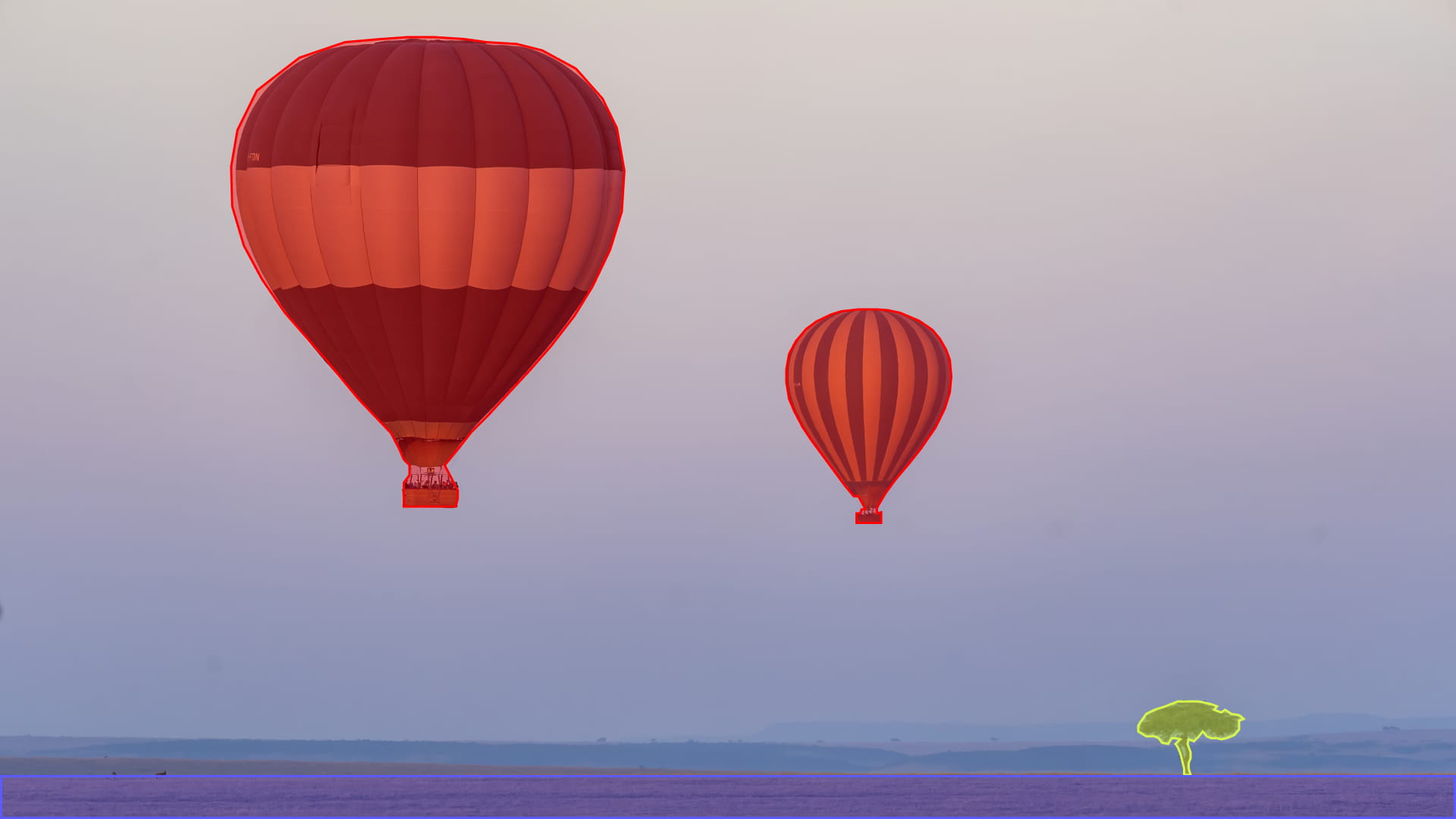
Segmentation models divide images into meaningful regions by assigning each pixel to a category (semantic segmentation), separating individual object instances (instance segmentation), or combining both approaches (panoptic segmentation).
Unlike classification models that label entire images, segmentation models understand spatial structure and object boundaries.
Which is the best image segmentation model?
No single best model exists, as it depends on your constraints.
SAM 3 handles zero-shot tasks across 270K+ concepts but runs 55× slower than YOLO11. Mask R-CNN achieves 43,425 citations for precision instance segmentation at ~5 FPS. DeepLabV3+ remains the proven CNN baseline for semantic tasks. YOLACT++ delivers 33 FPS for real-time applications.
For medical image segmentation models, nnU-Net dominates with 90%+ Dice scores through automatic pipeline configuration. That said, choose based on your speed-accuracy-domain triangle, not benchmark rankings.
What is the best method for image segmentation?
The method depends on your available training data and deployment requirements.
Foundation models like SAM 3 work zero-shot with text prompts but require fine-tuning for specialized domains (8-15% mIoU improvement).
Traditional supervised learning with models like Mask2Former or DeepLabV3+ needs 5K-100K labeled masks but achieves higher domain-specific accuracy. For medical imaging, nnU-Net's self-configuring pipeline handles 100-500 scans automatically.
Real-time applications favor single-stage methods like YOLACT++.
Is YOLO image segmentation?
YOLOv8 includes segmentation capabilities using YOLACT's prototype-coefficient architecture. It predicts 32 prototype masks and per-instance coefficients, then combines them via matrix multiplication.
YOLOv8-seg achieves competitive accuracy (0.90 precision/0.95 recall on agricultural datasets versus Mask R-CNN's 0.81/0.81) with faster inference. However, it's 5-6 AP points below Mask2Former on COCO benchmarks.
Which YOLO is best for segmentation?
YOLOv8-seg represents the current production choice, balancing speed and accuracy with architectural improvements over YOLACT++.
For cutting-edge real-time performance, RTMDet-Ins achieves 52.8% AP on COCO at 300+ FPS on RTX 3090. YOLO11 offers the latest detection capabilities but runs 55× faster than SAM 3 while sacrificing 12× boundary stability.
Choose YOLOv8-seg for general real-time segmentation, YOLACT++ for edge deployment (1,500 MB VRAM), RTMDet-Ins when maximum speed matters.
Written by
Karyna is the CEO of Label Your Data, a company specializing in data labeling solutions for machine learning projects. With a strong background in machine learning, she frequently collaborates with editors to share her expertise through articles, whitepapers, and presentations.





